Fenwick Tree
树状数组, 英文Fenwick Tree或Binary Index Tree, 是一种用来在$O(\log N)$时间复杂度内进行前缀和更新和查找的数据结构
Leetcode 307. Range Sum Query - Mutable
问题
Given an integer array nums, handle multiple queries of the following types:
- Update the value of an element in
nums. - Calculate the sum of the elements of
numsbetween indicesleftandrightinclusive whereleft <= right.
Implement the NumArray class:
NumArray(int[] nums)Initializes the object with the integer arraynums.void update(int index, int val)Updates the value ofnums[index]to beval.int sumRange(int left, int right)Returns the sum of the elements ofnumsbetween indicesleftandrightinclusive(i.e.nums[left] + nums[left + 1] + ... + nums[right]).
示例
Input
["NumArray", "sumRange", "update", "sumRange"]
[[[1, 3, 5]], [0, 2], [1, 2], [0, 2]]
Output
[null, 9, null, 8]
Explanation
NumArray numArray = new NumArray([1, 3, 5]);
numArray.sumRange(0, 2); // return 1 + 3 + 5 = 9
numArray.update(1, 2); // nums = [1, 2, 5]
numArray.sumRange(0, 2); // return 1 + 2 + 5 = 8
限制条件
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4-100 <= nums[i] <= 1000 <= index < nums.length-100 <= val <= 1000 <= left <= right < nums.length- At most
3 * 10^4calls will be made toupdateandsumRange.
题解
树状数组是线段树的一种特例,比线段树更为简单,但是只能求解特定的区间查询问题(前缀和问题)。
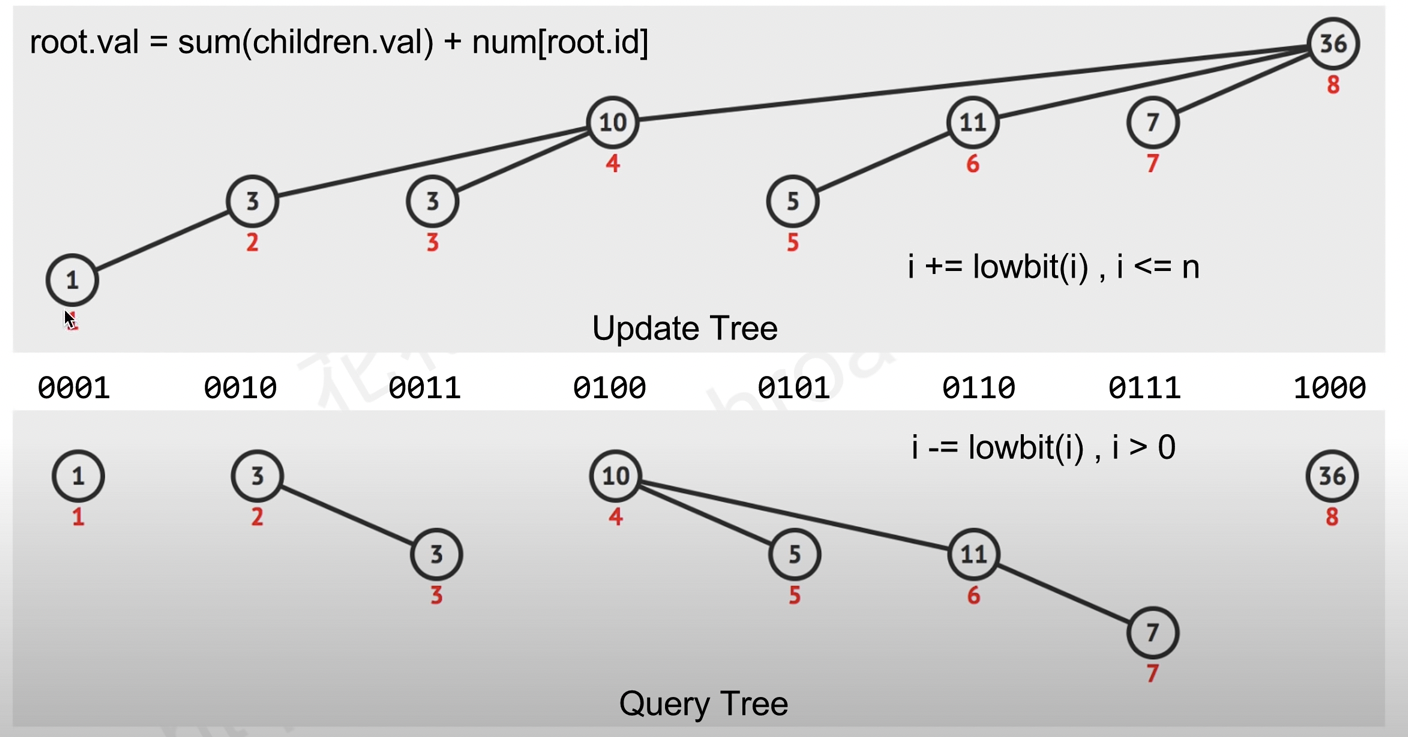
如上图所示,树状数组分为更新和查询两个步骤,并维护一个长度为n的sum数组(1-indexed),并假设原数组为num。我们可以得到以下映射关系:sum[1] = num[1], sum[2] = num[1] + num[2], sum[3] = num[3], sum[4] = num[1] + num[2] + num[3] + num[4], sum[5] = num[5], sum[6] = num[5] + num[6], sum[7] = num[7], sum[8] = num[1] + num[2] + num[3] + num[4] + num[5] + num[6] + num[7] + num[8], 以此类推,即当$$n = 2^k$$时$$sum[n] = sum(num[1:n])$$。可以理解为lowest bit 1越高,这个数在树中的层级越高,一个sum[10000](sum[16])就是由sum[1000] + sum[1100] + sum[1110] + sum[1111]组成,可以看到lowest bit 1越来越低。
Lowest bit 1快速的获取方法是x & (-x)。
代码如下:
def lowbit(x):
return x & (-x)
## Binary Index Tree
class BIT:
def __init__(self, nums):
self.nums = nums
self.sums = [0 for _ in range(len(nums) + 1)]
def update(self, i, delta):
while i <= len(self.nums):
self.sums[i] += delta
i += lowbit(i)
def query(self, i):
res = 0
while i > 0:
res += self.sums[i]
i -= lowbit(i)
return res
class NumArray:
def __init__(self, nums: List[int]):
self.bit = BIT(nums)
self.nums = nums
for i in range(1, len(nums) + 1):
self.bit.update(i, nums[i - 1])
def update(self, index: int, val: int) -> None:
self.bit.update(index + 1, val - self.nums[index])
self.nums[index] = val
def sumRange(self, left: int, right: int) -> int:
return self.bit.query(right + 1) - self.bit.query(left)
# Your NumArray object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = NumArray(nums)
# obj.update(index,val)
# param_2 = obj.sumRange(left,right)