Leetcode Notes
1. 动态规划
- 将原问题拆分为子问题
- 确认状态dp[i]代表什么
- 确认边界状态(初始条件)
- 状态转移方程
1.1 最长回文字串
leetcode 第五题 medium
问题:

采用动态规划的方法
首先可以发现,s.substring(i, j)是否为回文串取决于s.substring(i + 1, j - 1)与s.charAt(i)与s.charAt(j)是否相等,可以列出状态转移方程isPalindrome(s.substring(i, j)) = isPalindrome(s.substring(i + 1, j - 1)) && (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j))
其次找到边界条件,当s.length()<=1时一定是回文串,s.length()==2时是否为回文串取决于s.charAt(0) == s.charAt(1),s.length() == 3时取决于s.charAt(0) == s.charAt(2)
最后返回最长回文串,注意迭代的方式是从长度从短到长进行的
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int len = s.length();
if (len <= 1) {
return s;
}
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];
int maxLen = 1;
int startIndex = 0;
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
// 长度为1的字符串都是回文串
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
// 按照长度进行迭代
for (int length = 2; length <= len; length++) {
for (int left = 0; left <= len - length; left++) {
int right = left + length - 1;
if (c[left] != c[right]) {
dp[left][right] = false;
} else {
// 边界条件
if (length <= 3) {
dp[left][right] = true;
} else {
// 状态转移
dp[left][right] = dp[left + 1][right - 1];
}
}
if (dp[left][right]) {
if (length > maxLen) {
maxLen = length;
startIndex = left;
}
}
}
}
return s.substring(startIndex, startIndex + maxLen);
}
}
1.2 正则表达式匹配
hard
Given an input string (s) and a pattern (p), implement regular expression matching with support for ‘.’ and ‘*’ where:
‘.’ Matches any single character. ‘*’ Matches zero or more of the preceding element. The matching should cover the entire input string (not partial).
Example 1:
Input: s = “aa”, p = “a” Output: false Explanation: “a” does not match the entire string “aa”. Example 2:
Input: s = “aa”, p = “a*” Output: true Explanation: ‘*’ means zero or more of the preceding element, ‘a’. Therefore, by repeating ‘a’ once, it becomes “aa”. Example 3:
Input: s = “ab”, p = “.” Output: true Explanation: “.” means “zero or more (*) of any character (.)”. Example 4:
Input: s = “aab”, p = “cab” Output: true Explanation: c can be repeated 0 times, a can be repeated 1 time. Therefore, it matches “aab”. Example 5:
Input: s = “mississippi”, p = “mis*is*p*.” Output: false
采用动态规划,dp[i][j]为s的前i个长度的字符串能否被p的前j长度所匹配的布尔值。状态转移推导:
当p[j] == ‘*‘时,如果s[i]能够被p[j-1]匹配(s[i] == p[j-1]或p[j-1] == ‘.’)可以选择匹配s[i]也可以不匹配,即 $$ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] \ || \ dp[i][j-2] $$
否则如果s[i]不能被p[j-1]匹配,则 $$ dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-2] $$
否则如果p[j] != ‘*’, 则如果s[i]和p[j]匹配,那么 $$ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] $$
否则直接dp[i][j]为false
最终的状态转移方程为 $$ \begin{cases} if (p[j] = ‘*’) \begin{cases} dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] \ || \ dp[i][j-2],& matches(s[i], p[j-1])\ dp[i][j-2],& otherwise \end{cases}\ otherwise, \quad \begin{cases} dp[i-1][j-1], & matches(s[i], p[j])\ false, & otherwise \end{cases} \end{cases} $$
边界条件:
dp[0][0]=true,当i==0时,dp[i][j]取决于*,比如’a*‘和’a*a*‘能够匹配"",但是’a*a’不行
class Solution {
public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1][p.length() + 1];
dp[0][0] = true;
// 边界条件
if (p.length() >= 2) {
boolean flag = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= p.length() / 2; i++) {
if (p.charAt(i * 2 - 1) == '*' && flag) {
dp[0][i * 2] = true;
} else {
flag = false;
}
}
}
if (s.length() == 0 || p.length() == 0) {
return dp[s.length()][p.length()];
}
// 状态转移
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= p.length(); j++) {
if (p.charAt(j - 1) == '*') {
if (p.length() == 1) {return false;}
if (matches(s.charAt(i - 1), p.charAt(j - 2))) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] || dp[i][j - 2];
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2];
}
} else {
if (matches(s.charAt(i - 1), p.charAt(j - 1))) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
}
return dp[s.length()][p.length()];
}
private boolean matches(char s, char p) {
return (s == p || p == '.');
}
}
1.3 最长有效括号
Given a string containing just the characters ‘(’ and ‘)’, find the length of the longest valid (well-formed) parentheses substring.
Example 1:
Input: s = “(()” Output: 2 Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is “()”. Example 2:
Input: s = “)()())” Output: 4 Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is “()()”. Example 3:
Input: s = "" Output: 0
难度hard
设dp[i]为以s[i]结尾的最长有效字符串的长度,可知任何有效字符串都不可能以’(‘结尾,因此所有’(‘对应的dp[i]都为0。当s[i]==’)‘时,有几种可能性:
- s[i-1]为’(’,这时最后2个肯定是一个有效字符串,如果s[i-2]结尾的也是一个有效字符串,那么这两个字符串可以连起来,因此有dp[i] = dp[i - 2] + 2
- s[i-1]为’)’,这时如果去掉以s[i-1]结尾的最长有效字符串后的前面一个字符为’(’,就能和s[i]组成一个新的有效字符串,dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - dp[i - 1] - 2] + 2,否则dp[i] = 0
最后返回dp中的最大值
class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
int[] dp = new int[s.length()];
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (c[i] == ')') {
if (c[i - 1] == '(') {
dp[i] = i >= 2 ? (dp[i - 2] + 2) : 2;
} else if (c[i - 1] == ')') {
int temp = i - dp[i - 1] - 1;
if (temp >= 0) {
if (c[temp] == '(') {
if (temp - 1 >= 0) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[temp - 1] + 2;
}
else {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 2;
}
}
}
}
}
}
// return max of dp
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) {
if (dp[i] > ret) {
ret = dp[i];
}
}
return ret;
}
}
1.4 最大子序和
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] Output: 6 Explanation: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6. Example 2:
Input: nums = [1] Output: 1 Example 3:
Input: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8] Output: 23
采用动态规划,dp[i]表示以nums[i]结尾的子序中的最大和,可以让nums[i]和前面的最大子序合并,也可以自己成为一个新的子序,因此状态转移方程为dp[i] = max(nums[i] + dp[i - 1], nums[i])
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
int ret = dp[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
ret = Math.max(dp[i], ret);
}
return ret;
}
}
1.5 编辑距离
Given two strings word1 and word2, return the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following three operations permitted on a word:
Insert a character Delete a character Replace a character
Example 1:
Input: word1 = “horse”, word2 = “ros” Output: 3 Explanation: horse -> rorse (replace ‘h’ with ‘r’) rorse -> rose (remove ‘r’) rose -> ros (remove ’e’) Example 2:
Input: word1 = “intention”, word2 = “execution” Output: 5 Explanation: intention -> inention (remove ’t’) inention -> enention (replace ‘i’ with ’e’) enention -> exention (replace ’n’ with ‘x’) exention -> exection (replace ’n’ with ‘c’) exection -> execution (insert ‘u’)
可以用动态规划的方法解决。dp[i][j]代表word1的前i个字符转换为word2的前j个字符需要的最小edits,当word1[i] == word2[j]时,dp[i][j] == dp[i - 1][j - 1],当不相等时,可以用增加删除修改三种办法来进行转换。用修改的方法转换的话,就需要让word1的前i-1个字符转换到word2的前j - 1个字符,然后将word1的第i个字符转换为word2的第j个字符,因此dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1。用删除的方法转换的话,对于word1的前i-1个字符如果转换到word2的前j个字符的最小edits为dp[i-1][j],则删除word1的第i个字符,就可以得到相同的word2的前j个字符,即dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + 1。对于添加,dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + 1,而可以用这三种edits的任意一种,因此取他们的最小值。即 $$ dp[i][j] = \begin{cases} dp[i-1][j-1], & word1[i]==word2[j] \ min(dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j]) + 1 & otherwise \end{cases} $$
边界条件:dp[0][j]和dp[i][0]时,应该为j和i
1.7 打家劫舍
You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constraint stopping you from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security systems connected and it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses were broken into on the same night.
Given an integer array nums representing the amount of money of each house, return the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without alerting the police.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1] Output: 4 Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 1) and then rob house 3 (money = 3). Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4. Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,7,9,3,1] Output: 12 Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 2), rob house 3 (money = 9) and rob house 5 (money = 1). Total amount you can rob = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12.
设dp[i]为打劫前i个房子能够得到的最大金额,则如果打劫第i家,第i-1家不能打劫,因此打劫的总金额应该为dp[i-2]+nums[i]。(不打劫第i-1家的最大金额应该和只打劫前i-2家的最大金额相等)。如果不打劫第i家,则打劫的总金额为dp[i-1]。因此 $$ dp[i] = max(dp[i-2]+nums[i], dp[i-1]) $$
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 1) {
return nums[0];
} else if (nums.length == 2) {
return Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
}
int[] dp = new int[nums.length + 1];
dp[1] = nums[0];
dp[2] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 3; i <= nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i - 1], dp[i - 1]);
}
return dp[nums.length];
}
}
如果修改限制条件,将第一间房子和最后一间房子也作为邻居绕成一个圈,那么可以进行分类讨论,讨论不打劫第1户和打劫第1户的情况,这样的话dp[1]分别为0和nums[0],如果打劫了第1户就不能打劫最后一户,因此返回的应该是max(ret, dp[nums.length - 1])
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
int ret = 0;
// dp[i]表示打劫前i户最多的收入
int[] dp = new int[nums.length + 1];
// 不打劫第1户
dp[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i - 1], dp[i - 1]);
}
ret = Math.max(ret, dp[nums.length]);
// 打劫第1户
dp[1] = nums[0];
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i - 1], dp[i - 1]);
}
ret = Math.max(ret, dp[nums.length - 1]);
return ret;
}
1.8 扰乱字符串
设dp[i][j][len]为s1从第i个开始长度为len的子字符串sub1和s2从第j个字符开始长度为len的子字符串sub2是否为isScramble。
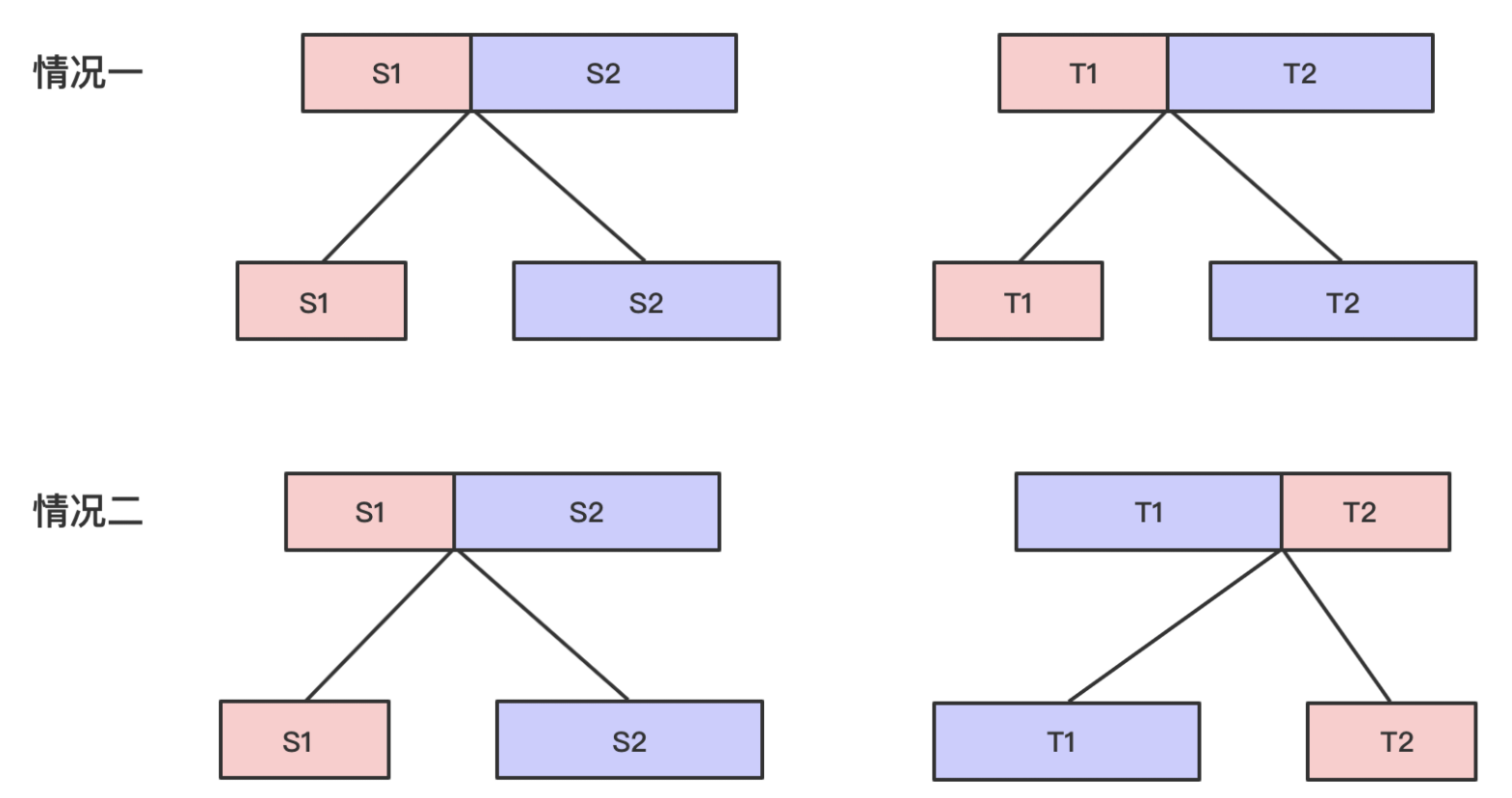
isScramble有两种情况为true,一种为isScramble(S1, T1) && isScramble(S2, T2), 另一种是isScramble(S1, T2) && isScramble(S2, T1)
边界条件为len==1的情况,此时只要字符相等就为true $$ dp[i][j][k] = (dp[i][j][w]\ &&\ dp[i+w][j+w][k-w])\ || \ (dp[i][j+k-w][w] \ && \ dp[i+w][j][k-w]) $$
最后返回dp[0][0][len]
class Solution {
public boolean isScramble(String s1, String s2) {
char[] c1 = s1.toCharArray();
char[] c2 = s2.toCharArray();
int len1 = c1.length;
int len2 = c2.length;
if (len1 != len2) return false;
boolean[][][] dp = new boolean[len1][len1][len1+1];
// 边界条件
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len2; j++) {
dp[i][j][1] = c1[i] == c2[j];
}
}
// 状态转移
for (int len = 2; len <= len1; len++) {
for (int i = 0; i <= len1 - len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= len2 - len; j++) {
for (int w = 1; w <= len - 1; w++) {
if ((dp[i][j][w] && dp[i + w][j + w][len - w]) || (dp[i][j + len - w][w] && dp[i + w][j][len - w])) {
dp[i][j][len] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][len1];
}
}
1.9 买卖股票的最佳时机III
You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
Find the maximum profit you can achieve. You may complete at most two transactions.
Note: You may not engage in multiple transactions simultaneously (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
Example 1:
Input: prices = [3,3,5,0,0,3,1,4] Output: 6 Explanation: Buy on day 4 (price = 0) and sell on day 6 (price = 3), profit = 3-0 = 3. Then buy on day 7 (price = 1) and sell on day 8 (price = 4), profit = 4-1 = 3. Example 2:
Input: prices = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: 4 Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4. Note that you cannot buy on day 1, buy on day 2 and sell them later, as you are engaging multiple transactions at the same time. You must sell before buying again. Example 3:
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1] Output: 0 Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0. Example 4:
Input: prices = [1] Output: 0
考虑采用动态规划,dp[i][j]表示第i天结束的状态为j的情况下的最大利润,j=0表示第一次买入,j=1表示第一次卖出,j=2表示第二次买入,j=3表示第二次卖出
状态转移:e.g. dp[i][0],即第i天结束完成了第一次买入,此时最大利润为max(第i-1天结束完成第一次买入的最大利润, -prices[i])
dp[i][1],即第i天完成第一次卖出,此时最大利润为第i天作了卖出操作产生的利润和没做卖出操作之前的最大利润的最大值,即max(dp[i-1][0] + prices[i], dp[i-1][1])
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
// 一天的操作总共有4种状态:第一次买入,第一次卖出,第二次买入,第二次卖出,每一次状态转换只能从前向后转换
int[][] dp = new int[prices.length + 1][4];
dp[0][0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
dp[0][2] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 1; i <= prices.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], -prices[i - 1]); // 第一次买入
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i - 1]); // 第一次卖出
dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i - 1]); // 第二次买入
dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2] + prices[i - 1]); // 第二次卖出
}
return Math.max(dp[prices.length][3], dp[prices.length][1]);
}
}
1.10 最后一块石头的重量
You are given an array of integers stones where stones[i] is the weight of the ith stone.
We are playing a game with the stones. On each turn, we choose any two stones and smash them together. Suppose the stones have weights x and y with x <= y. The result of this smash is:
If x == y, both stones are destroyed, and If x != y, the stone of weight x is destroyed, and the stone of weight y has new weight y - x. At the end of the game, there is at most one stone left.
Return the smallest possible weight of the left stone. If there are no stones left, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: stones = [2,7,4,1,8,1] Output: 1 Explanation: We can combine 2 and 4 to get 2, so the array converts to [2,7,1,8,1] then, we can combine 7 and 8 to get 1, so the array converts to [2,1,1,1] then, we can combine 2 and 1 to get 1, so the array converts to [1,1,1] then, we can combine 1 and 1 to get 0, so the array converts to [1], then that’s the optimal value. Example 2:
Input: stones = [31,26,33,21,40] Output: 5 Example 3:
Input: stones = [1,2] Output: 1
这道题可以转换为0-1背包问题然后用动态规划求解。要使最后一块石头的重量最小,其实就是把这堆石头分成重量最接近的两堆。因此转换为容量限制为sum / 2的背包问题,要使最终背包中的总质量最接近sum / 2.
public int lastStoneWeightII(int[] stones) {
// 转换为背包问题,背包中最多能装sum / 2,问最多大小
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < stones.length; i++) {
sum += stones[i];
}
// 动态规划,dp[i][j]表示选取前i块石头,限制为j的情况下的最高承载容量
int[][] dp = new int[stones.length + 1][sum / 2 + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= stones.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sum / 2; j++) {
if (j >= stones[i - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - stones[i - 1]] + stones[i - 1]);
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
return sum - 2 * dp[stones.length][sum / 2];
}
1.11 零钱兑换
You are given an integer array coins representing coins of different denominations and an integer amount representing a total amount of money.
Return the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
Example 1:
Input: coins = [1,2,5], amount = 11 Output: 3 Explanation: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1 Example 2:
Input: coins = [2], amount = 3 Output: -1 Example 3:
Input: coins = [1], amount = 0 Output: 0 Example 4:
Input: coins = [1], amount = 1 Output: 1 Example 5:
Input: coins = [1], amount = 2 Output: 2
采用动态规划,dp[i][j]为用k个coins[i]以及只用i之前面值的硬币的最小值组合起来的最小值。注意:由于当无法通过任何组合获取当前希望的总额j时,dp[i][j]为-1,这时如果取最小,那么res一定为-1,因此我们需要进行判断,当之前的dp[i-1][j-k*coins[i-1]]为-1时先跳过,当发现所有的都是-1时才会将dp[i][j]变为-1
边界条件为:除了dp[0][0]之外的dp[0][i]均为-1
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
// 完全背包问题
// dp[i][j]表示前i种面值的硬币兑换j总量的最少需要多少个硬币
int[][] dp = new int[coins.length + 1][amount + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
dp[0][i] = -1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= coins.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= amount; j++) {
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
boolean flag = false;
for (int k = 0; k <= j / coins[i - 1]; k++) {
if (dp[i - 1][j - k * coins[i - 1]] != -1) {
res = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - k * coins[i - 1]] + k, res);
flag = true;
}
}
// 无法组合为j总额
if (!flag) res = -1;
dp[i][j] = res;
}
}
return dp[coins.length][amount];
}
1.12 青蛙过河
A frog is crossing a river. The river is divided into some number of units, and at each unit, there may or may not exist a stone. The frog can jump on a stone, but it must not jump into the water.
Given a list of stones’ positions (in units) in sorted ascending order, determine if the frog can cross the river by landing on the last stone. Initially, the frog is on the first stone and assumes the first jump must be 1 unit.
If the frog’s last jump was k units, its next jump must be either k - 1, k, or k + 1 units. The frog can only jump in the forward direction.
Example 1:
Input: stones = [0,1,3,5,6,8,12,17] Output: true Explanation: The frog can jump to the last stone by jumping 1 unit to the 2nd stone, then 2 units to the 3rd stone, then 2 units to the 4th stone, then 3 units to the 6th stone, 4 units to the 7th stone, and 5 units to the 8th stone. Example 2:
Input: stones = [0,1,2,3,4,8,9,11] Output: false Explanation: There is no way to jump to the last stone as the gap between the 5th and 6th stone is too large.
此题采用动态规划,dp[i][j]表示能否以j步跳跃到i处,需要找到当前的位置stones[i]减去j步之后对应的index,如果能够找到这个index(存在可以正好跳j步跳到i处的某一个i之前的位置),则dp[i][j] = dp[index][j - 1] || dp[index][j] || dp[index][j + 1],即能用j-1步或j步或j+1步跳跃到index这个位置的可能性。寻找index可以用hashmap
public boolean canCross(int[] stones) {
int len = stones.length;
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len]; // dp[i][j]表示能否以j步跳跃到单位i处
if (stones[1] - stones[0] == 1) dp[1][1] = true;
else return false;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 用来存储stones[i]到index的映射
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
map.put(stones[i], i);
}
for (int i = 2; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < len; j++) {
int index = map.getOrDefault(stones[i] - j, -1);
if (index == -1) continue;
dp[i][j] = dp[index][j - 1] || dp[index][j] || (j == len - 1 ? false : dp[index][j + 1]);
}
}
boolean ret = false;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ret = ret || dp[len - 1][i];
}
return ret;
}
2 双指针
2.1 三数之和
Given an integer array nums, return all the triplets [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] such that i != j, i != k, and j != k, and nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0.
Notice that the solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] Example 2:
Input: nums = [] Output: [] Example 3:
Input: nums = [0] Output: []
这个问题如果直接暴力求解,复杂度为$O(N^3)$,可以考虑使用双指针,先进行排序,然后第一个指针a从0开始迭代,第二个指针b的初始位置在a+1,第三个指针c的初始位置在数组最后,如果nums[a]+nums[b]+nums[c]小于0,则指针b向后移动,若大于0则指针c向前移动,若等于0则加入结果中,等到b和c指针相交则a++。注意:为了防止结果重复,当指针abc在移动时如果发现移动的下一个目标和之前相等,那么跳过这个目标
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums.length < 3) {
return ret;
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
int a, b, c;
// sort out the input
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
pq.add(nums[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
nums[i] = pq.poll();
}
int prevA = nums[0] - 1;
int prevB = nums[0] - 1;
int prevC = nums[0] - 1;
for (a = 0; a < nums.length - 2; a++) {
if (nums[a] > 0 || nums[a] == prevA) {
continue;
}
prevA = nums[a];
prevB = nums[0] - 1;
prevC = nums[0] - 1;
b = a + 1;
c = nums.length - 1;
while (b != c) {
if (nums[b] == prevB) {
b++;
continue;
} else if (nums[c] == prevC) {
c--;
continue;
}
int sum = nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c];
if (sum == 0) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(nums[a]);
res.add(nums[b]);
res.add(nums[c]);
ret.add(res);
prevB = nums[b];
b++;
} else if (sum < 0) {
prevB = nums[b];
b++;
} else {
prevC = nums[c];
c--;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
}
2.2 长度最小的子数组
Given an array of positive integers nums and a positive integer target, return the minimal length of a contiguous subarray [numsl, numsl+1, …, numsr-1, numsr] of which the sum is greater than or equal to target. If there is no such subarray, return 0 instead.
Example 1:
Input: target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3] Output: 2 Explanation: The subarray [4,3] has the minimal length under the problem constraint. Example 2:
Input: target = 4, nums = [1,4,4] Output: 1 Example 3:
Input: target = 11, nums = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1] Output: 0
采用滑动窗口,用一个start指针和end指针分别表示子数组的起始索引和结束索引+1,即[start, end)。先不断移动end指针直到子数组和刚刚大于等于target,然后不断向右移动start指针直到子数组刚刚小于target,记录这个过程子数组的最小长度
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
// 滑动窗口
int start = 0;
int end = 0;
int sum = 0;
int ret = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (end < nums.length) {
while (sum < target) {
end += 1;
if (end > nums.length) break;
sum += nums[end - 1];
}
while (sum >= target) {
ret = Math.min(ret, end - start);
sum -= nums[start++];
}
}
return ret == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : ret;
}
2.3 寻找重复数
Given an array of integers nums containing n + 1 integers where each integer is in the range [1, n] inclusive.
There is only one repeated number in nums, return this repeated number.
You must solve the problem without modifying the array nums and uses only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,4,2,2] Output: 2 Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,1,3,4,2] Output: 3 Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1] Output: 1 Example 4:
Input: nums = [1,1,2] Output: 1
这道题可以用快慢指针的方法,由于存在重复的整数,因此每次跳到nums[i]位置必然会有一个loop,loop的入口的index就是重复的值。先让快指针一次跳两步,即fast = nums[nums[fast]],慢指针一次跳一步,即slow = nums[slow],当两个指针相遇时,说明两个指针已经进入了loop,这时将slow变为0,两个指针每次都跳一步,将在loop入口处相遇
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int slow = 0, fast = 0;
do {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[nums[fast]];
} while (slow != fast);
slow = 0;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[fast];
}
return slow;
}
3 回溯法
3.1 括号生成
Given n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3 Output: ["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"] Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: ["()"]
考虑使用深度优先搜索的回溯法,当剩下的左括号个数大于右括号个数时或者剩下的左括号个数和右括号个数小于0时剪枝
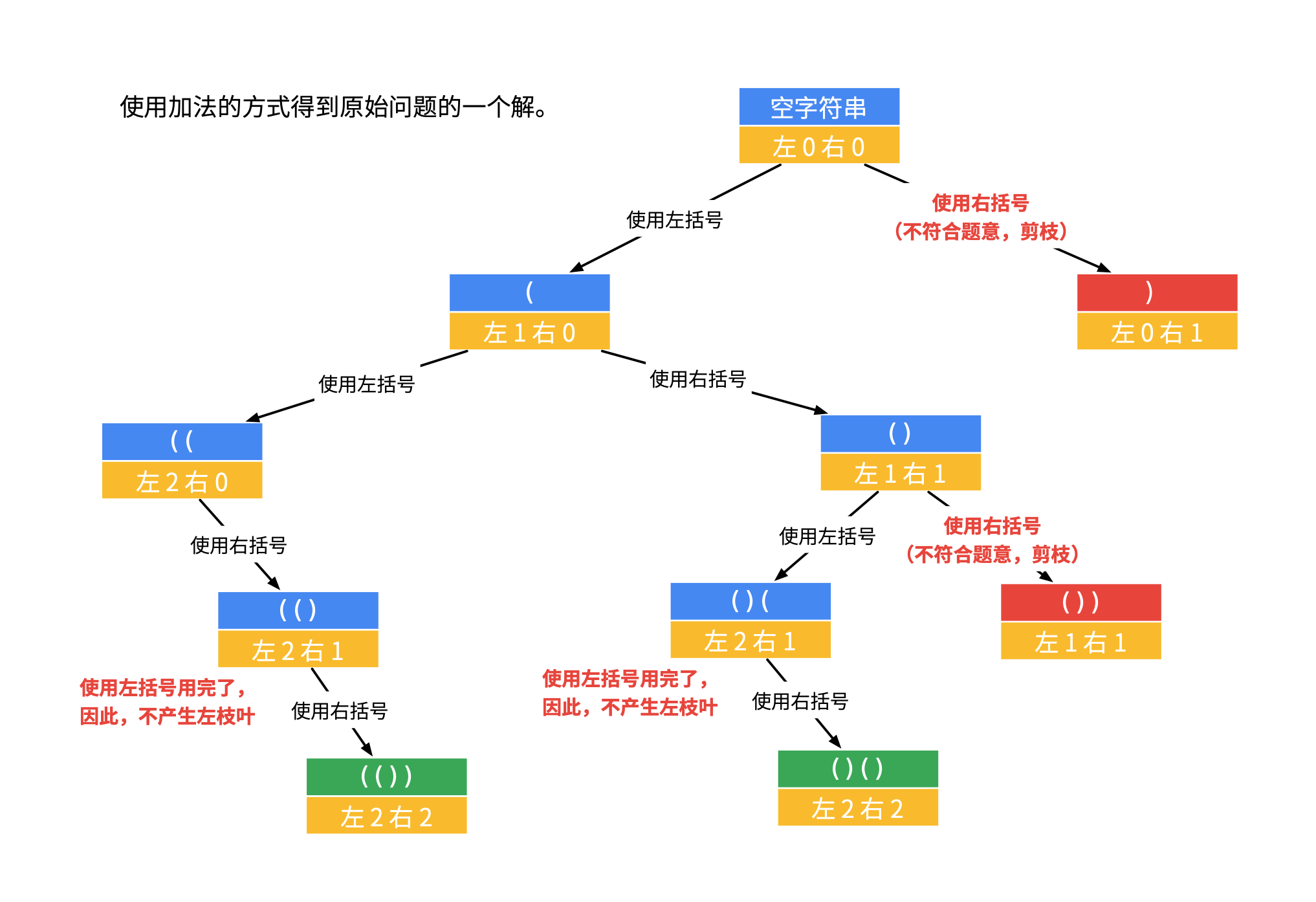
class Solution {
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
dfs("", n, n, ret);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(String curStr, int left, int right, List<String> ret) {
if (left > right || left < 0 || right < 0) {
return;
}
if (left == 0 && right == 0) {
ret.add(curStr);
return;
}
dfs(curStr + '(', left - 1, right, ret);
dfs(curStr + ')', left, right - 1, ret);
}
}
3.2 全排列II
Given a collection of numbers, nums, that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2] Output: [[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]] Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
解决方法:
使用深度优先搜索的回溯算法。本题的关键在于如何去重。可以先将nums进行排序,这样相同的元素就能排列在一起,当在进行dfs的时候需要加入path的元素和前一个元素相同并且前一个元素刚刚被pop出来(即nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false)时,说明一定会出现重复,此时进行剪枝。
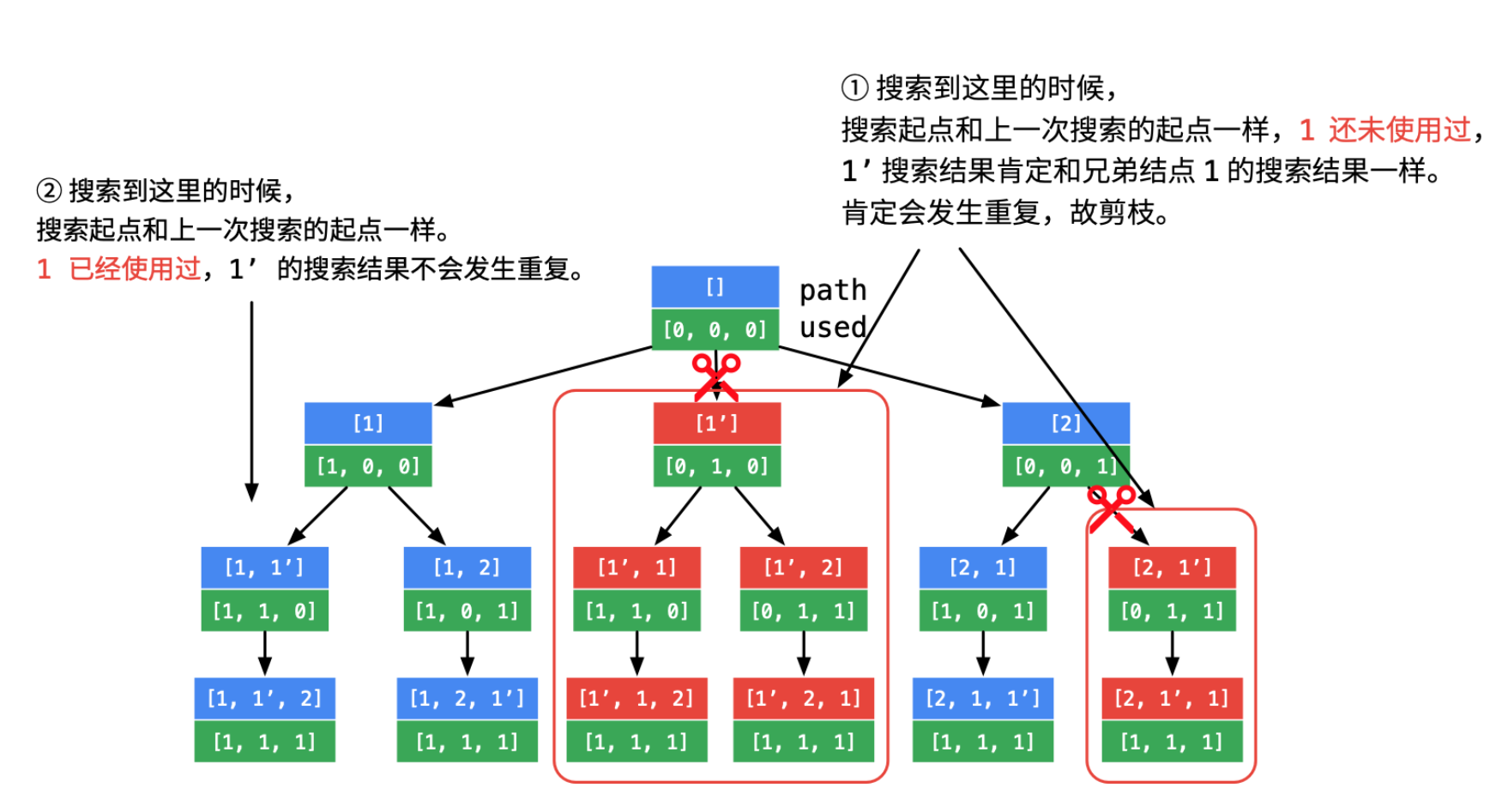
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.sort(nums);
dfs(nums, path, used, 0, ret);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, List<Integer> path, boolean[] used, int depth, List<List<Integer>> ret) {
if (depth == nums.length) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, path, used, depth + 1, ret);
used[i] = false;
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
3.3 N皇后
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens’ placement, where ‘Q’ and ‘.’ both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
Example 1:
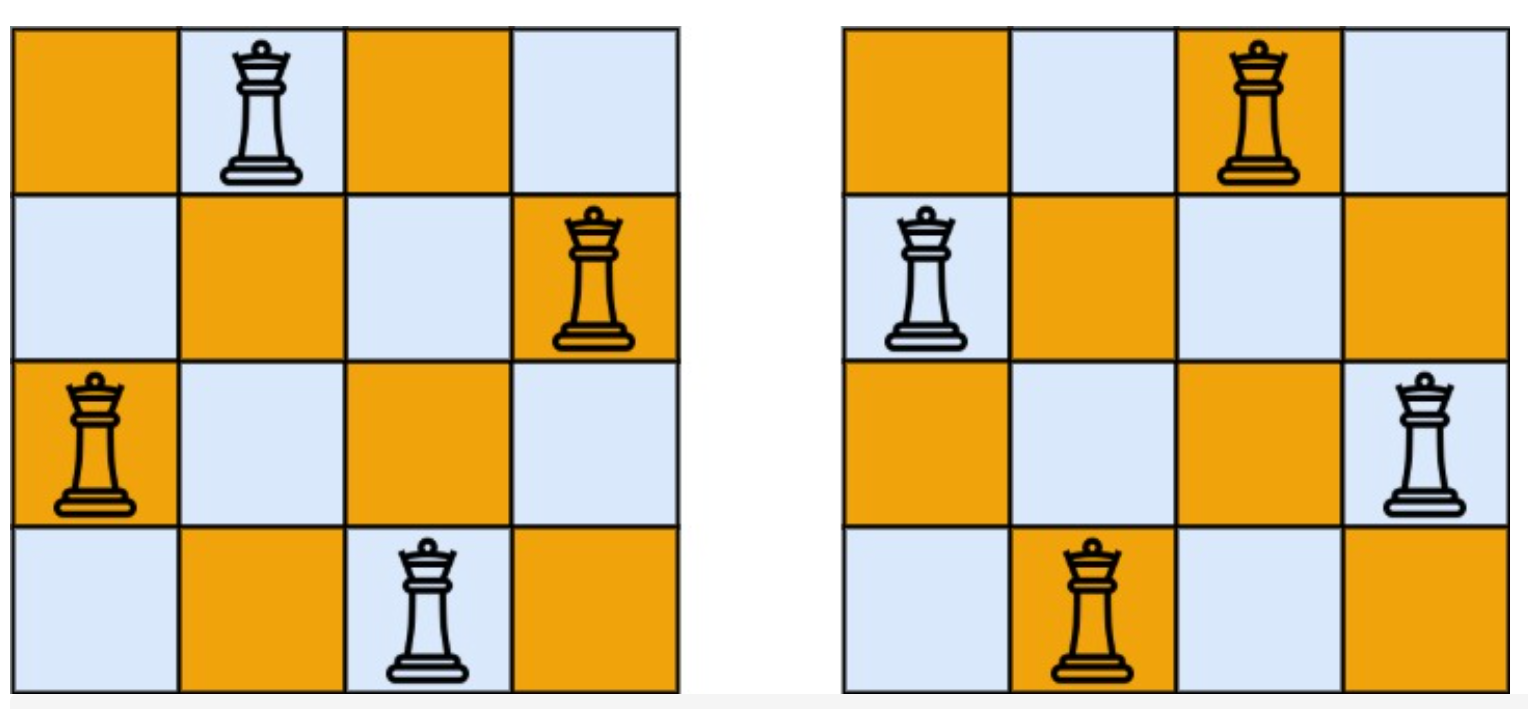
Input: n = 4 Output: [[".Q..","…Q",“Q…”,"..Q."],["..Q.",“Q…”,"…Q",".Q.."]] Explanation: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: [[“Q”]]
皇后可以横竖或沿斜边移动任意格数,因此每一行每一列一定只能有一个皇后。因此可以用一个长度为n的Int数组path来表示解法,每一个数组的元素代表这一行的皇后位于第几列,而每一个数组的Index代表第几行,比如[1, 3, 0, 2]代表上面图中的第一个解法。
考虑使用回溯法,由于已经满足了每一行每一列只有一个皇后,因此剪枝条件为两个皇后不能在同一个斜边上,即path中的任意两个元素的Index之差不能等于这两个元素的值的差
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used = new boolean[n];
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(path, used, res);
// 将解法转换为List<List<String>>的形式
List<List<String>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
char[] c = new char[n];
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
c[k] = '.';
}
c[res.get(i).get(j)] = 'Q';
list.add(new String(c));
}
ret.add(list);
}
return ret;
}
private void dfs(List<Integer> path, boolean[] used, List<List<Integer>> res) {
int len = used.length;
if (path.size() == len) {
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
boolean toSkip = false;
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
// 斜边剪枝
for (int j = 0; j < path.size(); j++) {
int temp = path.get(j);
if (Math.abs(temp - i) == Math.abs(j - path.size())) {
toSkip = true;
break;
}
}
if (toSkip) {
continue;
}
path.add(i);
used[i] = true;
dfs(path, used, res);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
3.4 格雷码
The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given an integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, return any sequence of gray code.
A gray code sequence must begin with 0.
Example 1:
Input: n = 2 Output: [0,1,3,2] Explanation: 00 - 0 01 - 1 11 - 3 10 - 2 [0,2,3,1] is also a valid gray code sequence. 00 - 0 10 - 2 11 - 3 01 - 1 Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: [0,1]
采用回溯法,每次变换对一位进行取反,公式为cur^(1«i)
class Solution {
public List<Integer> grayCode(int n) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[1<<n];
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(ret, 0, visited, n);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(List<Integer> ret, int cur, boolean[] visited, int n) {
if (visited[cur]) {
return;
}
ret.add(cur);
visited[cur] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(ret, cur^(1<<i), visited, n);
}
}
}
4 链表
4.1 反转链表II
Given the head of a singly linked list and two integers left and right where left <= right, reverse the nodes of the list from position left to position right, and return the reversed list.
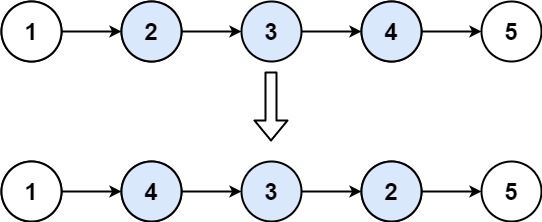
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4 Output: [1,4,3,2,5] Example 2:
Input: head = [5], left = 1, right = 1 Output: [5]
采用头插法:
分别定义两个指针,即g和p,g为leftNode的前一个ListNode(leftBefore),p为leftNode。将p后面的元素添加到g的后面,即头插法
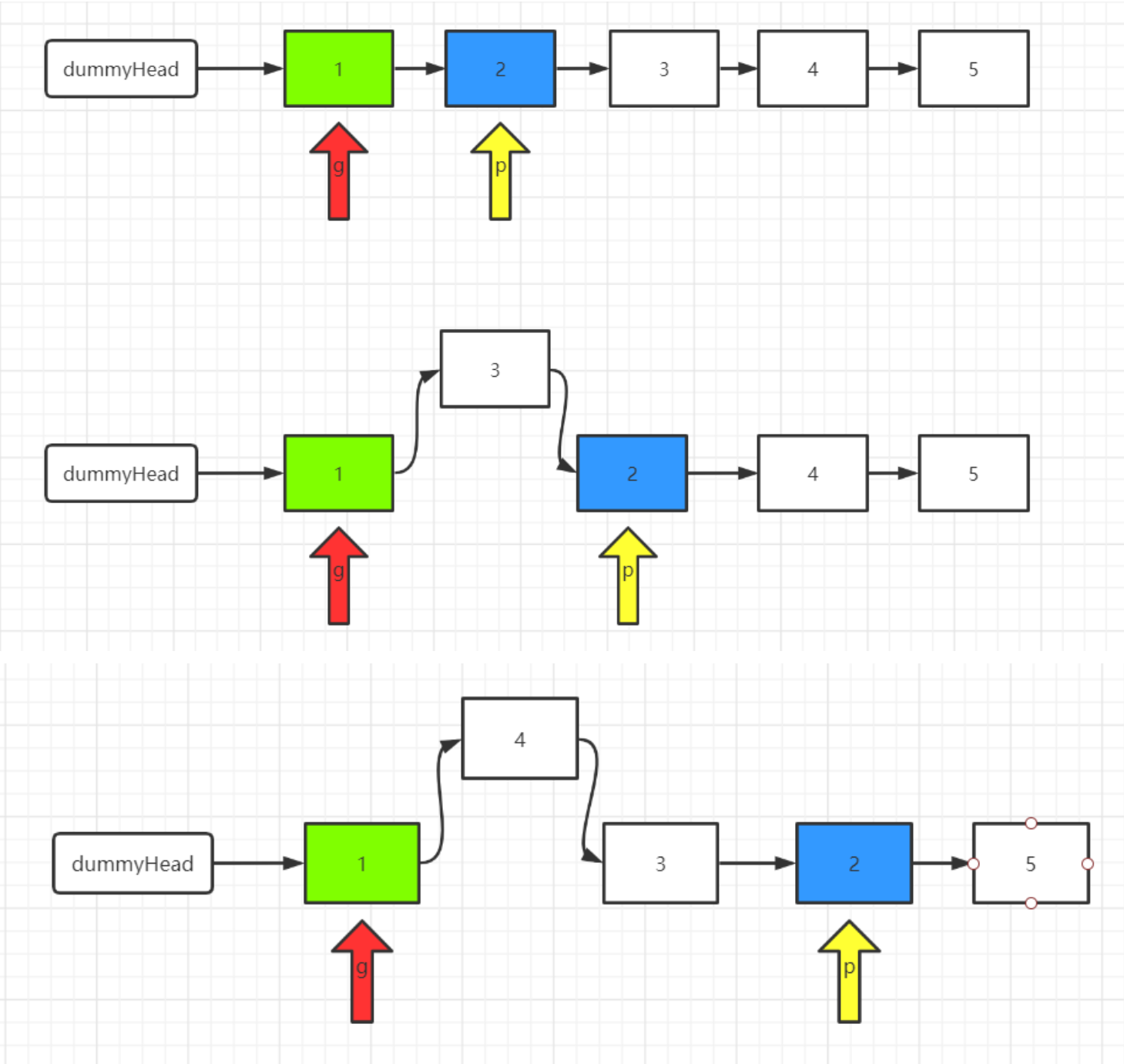
最后返回sentinel.next
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode leftBefore = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode leftNode = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode ptr = sentinel;
int i = 0;
while (ptr != null) {
if (i == left - 1) {
leftBefore = ptr;
}
if (i == left) {
leftNode = ptr;
}
if (i > right) {
break;
}
if (i > left) {
leftNode.next = ptr.next;
ptr.next = leftBefore.next;
leftBefore.next = ptr;
ptr = leftNode.next;
i++;
continue;
}
i++;
ptr = ptr.next;
}
return sentinel.next;
}
}
5 树
5.1 恢复二叉搜索树
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Follow up: A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward. Could you devise a constant space solution?
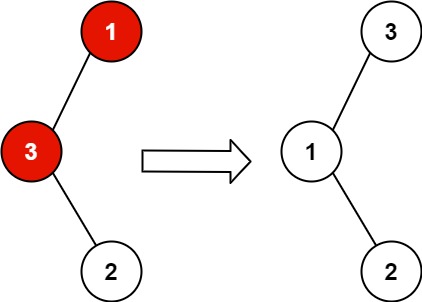
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2] Output: [3,1,null,null,2] Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:
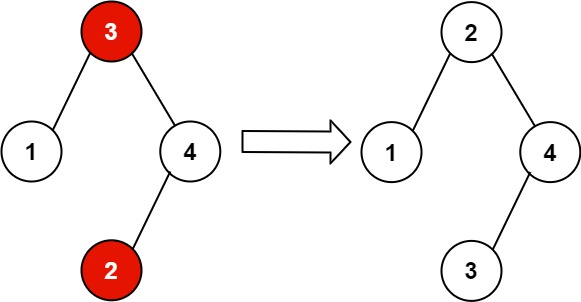
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3] Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
采用Morris遍历,其算法如下
记录当前节点为cur
如果cur无左节点,则cur向右移动(cur = cur.right)
如果cur有左节点,则找到cur左子树上最右的节点(即中序遍历中的cur的前一个节点),记为mostright
- 如果mostright的right指针指向空,让其指向cur,cur向左移动(cur = cur.left)
- 如果mostright的right指针指向cur,让其指向空,cur向右移动(cur = cur.right)
这道题关键是要找到两个需要交换的节点。先采用Morris算法进行中序遍历,当发现当前值curVal小于等于前值predVal时,说明出现问题,比如Example1中的中序遍历结果为321,则这样的问题分别在遍历到2和1时出现了2次,这时需要将第一次出现问题的前面一个Node和第二次出现问题的当前node,即3和1这两个Node进行交换。如果中序遍历时问题只出现了1次,比如example2中的中序遍历结果为1324,在遍历到2时出现了问题,则只需要将3和2这两个节点进行交换即可。
class Solution {
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
// inorder traverse using Morris algorithm
TreeNode cur = root;
int predVal = 0;
TreeNode preNode = null;
int curVal = 0;
boolean flag = false;
TreeNode swap1 = null;
TreeNode swap2 = null;
while (cur != null) {
curVal = cur.val;
if (flag && predVal >= curVal) {
// the first time problem occurs
if (swap1 == null) {
swap1 = preNode;
swap2 = cur;
} else {
// the second time problem occurs
swap2 = cur;
}
}
if (cur.left != null) {
// find the rightmost node on the left
TreeNode mostRight = cur.left;
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
} else {
mostRight.right = null;
predVal = cur.val;
preNode = cur;
if (!flag) flag = true;
cur = cur.right;
}
} else {
predVal = cur.val;
preNode = cur;
if (!flag) flag = true;
cur = cur.right;
}
}
int temp = swap1.val;
swap1.val = swap2.val;
swap2.val = temp;
}
}
5.2 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
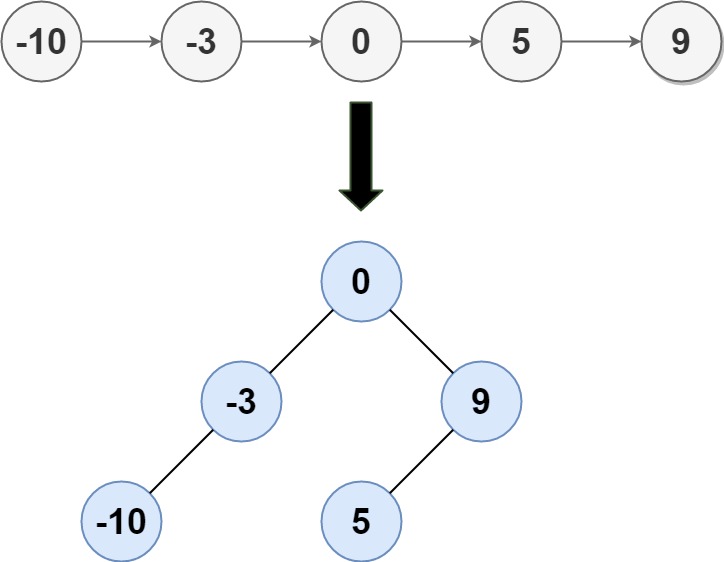
Example 1:
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST. Example 2:
Input: head = [] Output: [] Example 3:
Input: head = [0] Output: [0] Example 4:
Input: head = [1,3] Output: [3,1]
为了实现平衡二叉搜索树,需要将root节点的值设置为链表中间节点的值,然后左节点为中间节点左边部分,右节点为中间节点右边部分。
这道题的难点在于如何高效地找到中间节点,这里用了一个快指针和一个慢指针,快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步,这样当快指针遍历完链表之后,慢指针正好指向中间节点
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
// 双指针,快指针一次走2步,慢指针一次走一步,这样快指针遍历完List之后慢指针指向list中间的node
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode pred = null;
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
if (fast == null) {
break;
} else {
fast = fast.next;
}
pred = slow;
slow = slow.next;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(slow.val);
if (pred == null) {
root.left = null;
} else {
pred.next = null;
root.left = sortedListToBST(head);
}
root.right = sortedListToBST(slow.next);
return root;
}
}
6 字典树
6.1 实现字典树
A trie (pronounced as “try”) or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker.
Implement the Trie class:
Trie() Initializes the trie object. void insert(String word) Inserts the string word into the trie. boolean search(String word) Returns true if the string word is in the trie (i.e., was inserted before), and false otherwise. boolean startsWith(String prefix) Returns true if there is a previously inserted string word that has the prefix prefix, and false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input [“Trie”, “insert”, “search”, “search”, “startsWith”, “insert”, “search”] [[], [“apple”], [“apple”], [“app”], [“app”], [“app”], [“app”]] Output [null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
Explanation Trie trie = new Trie(); trie.insert(“apple”); trie.search(“apple”); // return True trie.search(“app”); // return False trie.startsWith(“app”); // return True trie.insert(“app”); trie.search(“app”); // return True
class Trie {
private class TrieNode {
boolean exists;
TrieNode[] next;
TrieNode() {
exists = false;
next = new TrieNode[26];
}
}
TrieNode head;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
head = new TrieNode();
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode ptr = head;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int index = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (ptr.next[index] == null) {
ptr.next[index] = new TrieNode();
}
ptr = ptr.next[index];
}
ptr.exists = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode ptr = head;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int index = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (ptr.next[index] == null) {
return false;
}
ptr = ptr.next[index];
}
return ptr.exists;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode ptr = head;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
int index = prefix.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (ptr.next[index] == null) {
return false;
}
ptr = ptr.next[index];
}
return true;
}
}
6.2 数组中两个数的最大异或值
Given an integer array nums, return the maximum result of nums[i] XOR nums[j], where 0 ≤ i ≤ j < n.
要求时间复杂度O(n)
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,10,5,25,2,8] Output: 28 Explanation: The maximum result is 5 XOR 25 = 28. Example 2:
Input: nums = [0] Output: 0 Example 3:
Input: nums = [2,4] Output: 6 Example 4:
Input: nums = [8,10,2] Output: 10 Example 5:
Input: nums = [14,70,53,83,49,91,36,80,92,51,66,70] Output: 127
建立字典树,将每个数表示为31个二进制位,为了获得最大异或值,需要让最终的结果x的高位为1。假设已经确定了其中一个数aj,需要确定另一个被异或的数ai,当aj的某个高位k为1时,为了使得最终被异或的结果为1,那么ai的这一位必须为0。最终遍历字典树,得到使得异或结果最大的那个数ai。对数组中的所有数进行遍历取aj,最终的时间复杂度为O(N*log(C)),其中C为数组中可以取到的最大的数,本例中为31
class Solution {
private class Node {
Node left;
Node right;
}
private class Trie {
Node head;
Trie() {
head = new Node();
}
void insert(int n) {
Node ptr = head;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {
int index = (n >> i) & 1;
if (index == 1) {
if (ptr.right == null) {
ptr.right = new Node();
}
ptr = ptr.right;
} else {
if (ptr.left == null) {
ptr.left = new Node();
}
ptr = ptr.left;
}
}
}
}
public int findMaximumXOR(int[] nums) {
int ret = 0;
Trie trie = new Trie();
// build the trie
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
trie.insert(nums[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int a = nums[i];
int b = 0;
Node ptr = trie.head;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--) {
int index = (a >> j) & 1;
if (index == 1) {
if (ptr.left != null) {
ptr = ptr.left;
b = b * 2 + 1;
} else {
ptr = ptr.right;
b = b * 2;
}
} else {
if (ptr.right != null) {
ptr = ptr.right;
b = b * 2 + 1;
} else {
ptr = ptr.left;
b = b * 2;
}
}
}
ret = Math.max(ret, b);
}
return ret;
}
}
7 排序算法
7.1 数组中的第k个最大元素(堆排序)
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the kth largest element in the array.
Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2 Output: 5 Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6], k = 4 Output: 4
采用最大堆在数组原地进行heapify,heapify的方法是从最底层往上进行heapify,寻找每个树中最大的那个节点,放到这个树的root上,然后对交换了的子节点进行递归Heapify(因为子节点形成的堆结构可能已经被这个交换操作给破坏了)
删除节点的方法是将第一个节点和最后一个节点(heapsize维护)进行交换,然后对第一个节点进行heapify
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
buildMaxHeap(nums);
int heapSize = nums.length;
// 删除堆顶元素
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
swap(nums, 0, heapSize - 1);
maxHeapify(nums, 0, --heapSize);
}
return nums[0];
}
private void buildMaxHeap(int[] nums) {
for (int i = nums.length / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
// 从底层到高层进行heapify
maxHeapify(nums, i, nums.length);
}
}
private void maxHeapify(int[] nums, int root, int heapSize) {
// 左右节点的Index
int left = 2 * root + 1;
int right = 2 * root + 2;
int max = root;
// 寻找root、left、right中最大的那个节点,将这个节点和root互换
if (left < heapSize && nums[left] > nums[max]) {
max = left;
}
if (right < heapSize && nums[right] > nums[max]) {
max = right;
}
if (max != root) {
swap(nums, max, root);
maxHeapify(nums, max, heapSize);
}
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b) {
int temp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = temp;
}
8 线段树
8.1区域和检索
Given an integer array nums, handle multiple queries of the following types:
Update the value of an element in nums. Calculate the sum of the elements of nums between indices left and right inclusive where left <= right. Implement the NumArray class:
NumArray(int[] nums) Initializes the object with the integer array nums. void update(int index, int val) Updates the value of nums[index] to be val. int sumRange(int left, int right) Returns the sum of the elements of nums between indices left and right inclusive (i.e. nums[left] + nums[left + 1] + … + nums[right]).
Example 1:
Input [“NumArray”, “sumRange”, “update”, “sumRange”] [[[1, 3, 5]], [0, 2], [1, 2], [0, 2]] Output [null, 9, null, 8]
Explanation NumArray numArray = new NumArray([1, 3, 5]); numArray.sumRange(0, 2); // return 1 + 3 + 5 = 9 numArray.update(1, 2); // nums = [1, 2, 5] numArray.sumRange(0, 2); // return 1 + 2 + 5 = 8
class NumArray {
int[] tree;
int[] nums;
int n;
private void buildTree(int node, int start, int end) {
// 构建线段树,假如每个线段[l,r]位于tree[i],那么[l, (l+r)/2]位于tree[i*2+1],[(l+r)/2+1, r]位于tree[i*2+2],根节点从tree[0]开始
if (start == end) {
tree[node] = nums[start];
return;
}
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
int left = node * 2 + 1;
int right = node * 2 + 2;
buildTree(left, start, mid);
buildTree(right, mid + 1, end);
tree[node] = tree[left] + tree[right];
}
private void updateTree(int idx, int node, int val, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) return;
if (start == end) {
nums[idx] = val;
tree[node] = val;
} else {
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
int left = node * 2 + 1;
int right = node * 2 + 2;
if (idx >= start && idx <= mid)
updateTree(idx, left, val, start, mid);
else
updateTree(idx, right, val, mid + 1, end);
tree[node] = tree[left] + tree[right];
}
}
private int query(int L, int R, int node, int start, int end) {
if (L > end || R < start) return 0;
if (start == end) return tree[node];
if (L <= start && end <= R) return tree[node];
else {
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
int left = node * 2 + 1;
int right = node * 2 + 2;
int ls = query(L, R, left, start, mid);
int rs = query(L, R, right, mid + 1, end);
return ls + rs;
}
}
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
n = nums.length;
if (n == 0) return;
this.nums = nums;
tree = new int[n * 4];
buildTree(0, 0, n - 1);
}
public void update(int i, int val) {
updateTree(i, 0, val, 0, n - 1);
}
public int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return query(i, j, 0, 0, n - 1);
}
}
9 树状数组
9.1 计算右侧小于当前元素的个数
You are given an integer array nums and you have to return a new counts array. The counts array has the property where counts[i] is the number of smaller elements to the right of nums[i].
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,2,6,1] Output: [2,1,1,0] Explanation: To the right of 5 there are 2 smaller elements (2 and 1). To the right of 2 there is only 1 smaller element (1). To the right of 6 there is 1 smaller element (1). To the right of 1 there is 0 smaller element. Example 2:
Input: nums = [-1] Output: [0] Example 3:
Input: nums = [-1,-1] Output: [0,0]
这道题要求时间复杂度不能大于等于O(N^2)。考虑采用树状数组的方法。首先将nums离散化,即将Nums去重后进行排序得到一个新的数组,建立nums和这个新数组的映射关系,这样就形成了一个桶,可以计算每个值出现的次数并求前缀和快速得到某个时刻nums中小于某个值的元素个数。这个前缀和数组以树状数组的形式存储,从而能够以O(logN)的速度进行update和query。
树状数组的建立方法见https://www.cnblogs.com/xenny/p/9739600.html
nums从后往前遍历,先得到此时prefix数组中小于nums[i]的个数(通过query函数),然后通过update函数增加nums[i]的值对应于prefix数组中的各个位置的值。
public List<Integer> countSmaller(int[] nums) {
// 去重排序映射
int[] nums2 = Arrays.copyOf(nums, nums.length);
Arrays.sort(nums2);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); // list为去重排序后的数组
list.add(nums2[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums2[i] != nums2[i - 1]) {
list.add(nums2[i]);
}
}
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // map为nums[i] -> list中的index的映射
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
map.put(list.get(i), i);
}
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int[] prefix = new int[list.size() + 1];
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int index = map.get(nums[i]) + 1; // prefix的index从1开始
ret.add(0, query(index - 1, prefix));
update(index, prefix);
}
return ret;
}
private void update(int index, int[] prefix) {
while (index < prefix.length) {
prefix[index]++;
index += lowbit(index);
}
}
private int query(int index, int[] prefix) {
int ret = 0;
while (index > 0) {
ret += prefix[index];
index -= lowbit(index);
}
return ret;
}
// 返回x的二进制的最右边的1保持剩下位数全部变0的整数
private int lowbit(int x) {
return x & (-x);
}
10 单调栈
10.1 去除重复字母
Given a string s, remove duplicate letters so that every letter appears once and only once. You must make sure your result is the smallest in lexicographical order among all possible results.
Example 1:
Input: s = “bcabc” Output: “abc” Example 2:
Input: s = “cbacdcbc” Output: “acdb”
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 104 s consists of lowercase English letters.
这道题可以使用单调栈。如果要使字符串字典序最小,则在从左往右遍历的过程中,需要删除每一个满足s[i] > s[i + 1]的s[i],除非删除这个会导致后面的字符串中再也不会出现s[i]这个值的元素(即需要满足every letter appears once),这是贪心算法的体现。单调栈中维护的是当前去除了满足条件的字符之后的字符串,大约保证栈顶到栈底是从大到小的,因此在遍历的过程中,需要将每个s[i]和栈顶元素进行比较,如果小于栈顶元素而且能够将栈顶元素删除,那么就pop(),然后将s[i]入栈,否则如果栈中已经出现了s[i]对应的字符,则不能将s[i]入栈(要满足every letter appears only once),最后栈中的结果就是返回值
public String smallestSubsequence(String s) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int[] nums = new int[26];
boolean[] contains = new boolean[26]; // 表示某个字符是否在栈中出现
// 统计每个字符出现的次数
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
nums[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
nums[s.charAt(i) - 'a']--; // s[i]这个字符出现的次数减一
// 如果栈中已经有了这个字符,就不能再入栈了,否则会造成重复
if (contains[s.charAt(i) - 'a']) {
continue;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
// 重复将s[i]和栈顶元素比较,如果比栈顶元素小而且删除当前的栈顶元素不会导致后面栈顶元素再也无法出现,那么删除这个栈顶元素
char c = stack.peek();
if (s.charAt(i) < c && nums[c - 'a'] != 0) {
stack.pop();
contains[c - 'a'] = false;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 入栈
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
contains[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] = true;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
sb.insert(0, stack.pop());
}
return sb.toString();
}
10.2 拼接最大数
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2 of lengths m and n respectively. nums1 and nums2 represent the digits of two numbers. You are also given an integer k.
Create the maximum number of length k <= m + n from digits of the two numbers. The relative order of the digits from the same array must be preserved.
Return an array of the k digits representing the answer.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [3,4,6,5], nums2 = [9,1,2,5,8,3], k = 5 Output: [9,8,6,5,3] Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [6,7], nums2 = [6,0,4], k = 5 Output: [6,7,6,0,4] Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [3,9], nums2 = [8,9], k = 3 Output: [9,8,9]
思路:先设定nums1中最多取i个,nums2中最多取k - i个数,分别利用单调栈求得最大子序列,然后将这两个最大子序列merge()为一个序列。对所有的i重复上述操作(i要包括0和k),返回上述最大子序列的最大值
public int[] maxNumber(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>() { {
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
add(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
}};
// 单调栈
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
if (i > nums1.length || k - i > nums2.length) continue;
// i表示nums1取的数组长度, nums2的数组长度应该为k - i
List<Integer> list1 = maxnum(nums1, i);
List<Integer> list2 = maxnum(nums2, k - i);
List<Integer> temp = merge(list1, list2);
boolean flag = true;
// 计算最大的子序列
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
if (list.get(j) > temp.get(j)) {
flag = false;
break;
} else if (list.get(j) < temp.get(j)) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
list = temp;
}
}
int[] ret = new int[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ret[i] = list.get(i);
}
return ret;
}
// 单调栈求解长度为k的num最大子序列
private List<Integer> maxnum(int[] num, int k) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int len = num.length;
if (k >= len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ret.add(num[i]);
}
return ret;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int temp = stack.peek();
if (len - i + stack.size() - 1 >= k && num[i] > temp) {
stack.pop();
} else {
break;
}
}
stack.push(num[i]);
}
int temp = stack.size();
for (int i = 0; i < temp - k; i++) {
stack.pop();
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ret.add(0, stack.pop());
}
return ret;
}
// 将两个序列合并为最大序列
private List<Integer> merge(List<Integer> l1, List<Integer> l2) {
int p1 = 0, p2 = 0;
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while (p1 < l1.size() && p2 < l2.size()) {
int i1 = l1.get(p1);
int i2 = l2.get(p2);
if (i1 > i2) {
ret.add(l1.get(p1++));
} else if (i1 < i2) {
ret.add(l2.get(p2++));
} else {
if (compare(p1, p2, l1, l2) > 0) {
ret.add(l1.get(p1++));
} else {
ret.add(l2.get(p2++));
}
}
}
while (p1 < l1.size()) {
ret.add(l1.get(p1++));
}
while (p2 < l2.size()) {
ret.add(l2.get(p2++));
}
return ret;
}
// 比较两个序列大小
private int compare (int i1, int i2, List<Integer> l1, List<Integer> l2) {
while (i1 < l1.size() && i2 < l2.size()) {
if (l1.get(i1) > l2.get(i2)) {
return 1;
} else if (l1.get(i1) < l2.get(i2)) {
return -1;
} else {
i1++;
i2++;
}
}
return l1.size() - i1 - (l2.size() - i2);
}
10.3 接雨水
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:

Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] Output: 6 Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped. Example 2:
Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5] Output: 9
这道题可以采用单调栈来做,维护一个单调递减栈,栈中为index,栈顶index对应的height低于栈底index对应的height,当遇到了一个高于当前栈顶的砖块,说明形成了一个可以接雨水的低洼处,接雨水的底部高度为当前栈顶index对应的值,两边高度为height[i]和pop掉栈顶之后下一个栈顶对应高度的最小值,相乘即得到这个低洼可以接的雨水的量
public int trap(int[] height) {
// 单调栈,栈底到栈顶的height val单调递减
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]) {
int bottom = height[stack.pop()]; // 接雨水的底的高度
if (stack.isEmpty()) break;
ret += (Math.min(height[i], height[stack.peek()]) - bottom) * (i - stack.peek() - 1);
}
stack.push(i);
}
return ret;
}
11 并查集
并查集(union find)支持disjoint union和find两种操作,标准的Python模板为
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.parent = [i for i in range(n)]
def find(self, x):
if self.parent[x] == x:
return x
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def union(self, x, y):
root1, root2 = self.find(x), self.find(y)
if (root1 != root2):
self.parent[root1] = root2
11.1 除法求值
You are given an array of variable pairs equations and an array of real numbers values, where equations[i] = [Ai, Bi] and values[i] represent the equation Ai / Bi = values[i]. Each Ai or Bi is a string that represents a single variable.
You are also given some queries, where queries[j] = [Cj, Dj] represents the jth query where you must find the answer for Cj / Dj = ?.
Return the answers to all queries. If a single answer cannot be determined, return -1.0.
Note: The input is always valid. You may assume that evaluating the queries will not result in division by zero and that there is no contradiction.
Example 1:
Input: equations = [[“a”,“b”],[“b”,“c”]], values = [2.0,3.0], queries = [[“a”,“c”],[“b”,“a”],[“a”,“e”],[“a”,“a”],[“x”,“x”]] Output: [6.00000,0.50000,-1.00000,1.00000,-1.00000] Explanation: Given: a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0 queries are: a / c = ?, b / a = ?, a / e = ?, a / a = ?, x / x = ? return: [6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ] Example 2:
Input: equations = [[“a”,“b”],[“b”,“c”],[“bc”,“cd”]], values = [1.5,2.5,5.0], queries = [[“a”,“c”],[“c”,“b”],[“bc”,“cd”],[“cd”,“bc”]] Output: [3.75000,0.40000,5.00000,0.20000] Example 3:
Input: equations = [[“a”,“b”]], values = [0.5], queries = [[“a”,“b”],[“b”,“a”],[“a”,“c”],[“x”,“y”]] Output: [0.50000,2.00000,-1.00000,-1.00000]
这道题实际上是一个有向图问题,equation的左右两边是两个顶点,从一个顶点到另一个顶点的权重就是value,为了判断query的值是否能被确定,采用并查集,当两个顶点的root为同一个时说明query能够被确定,值为权重之比。
在进行union时,要寻找两个顶点的根节点,并将后一个顶点的根节点变为前一个根节点的根节点
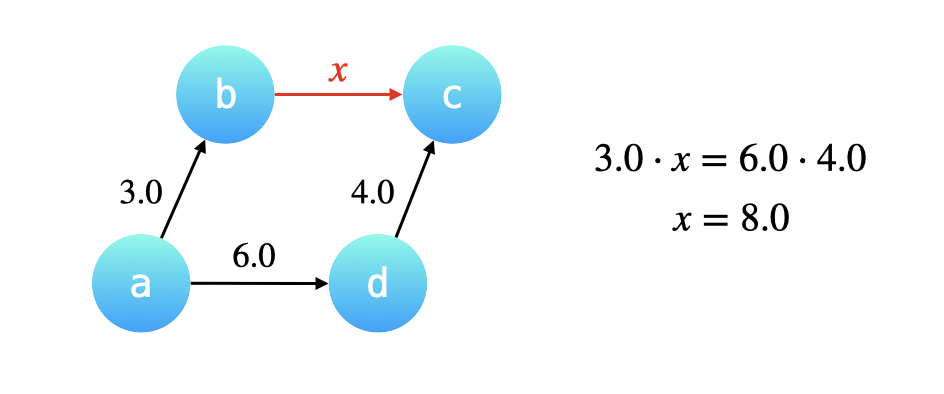
比如已知a -> b = 3.0, d -> c = 4.0,对a和d进行union,其中权值为6.0,只需要将c变为b的根节点,并且将b的权值x变为6.0*4.0/3.0即可
在查询节点的过程中,有可能会出现直接父节点还存在根节点的问题,这样可能造成权值直接相除有问题,比如下图
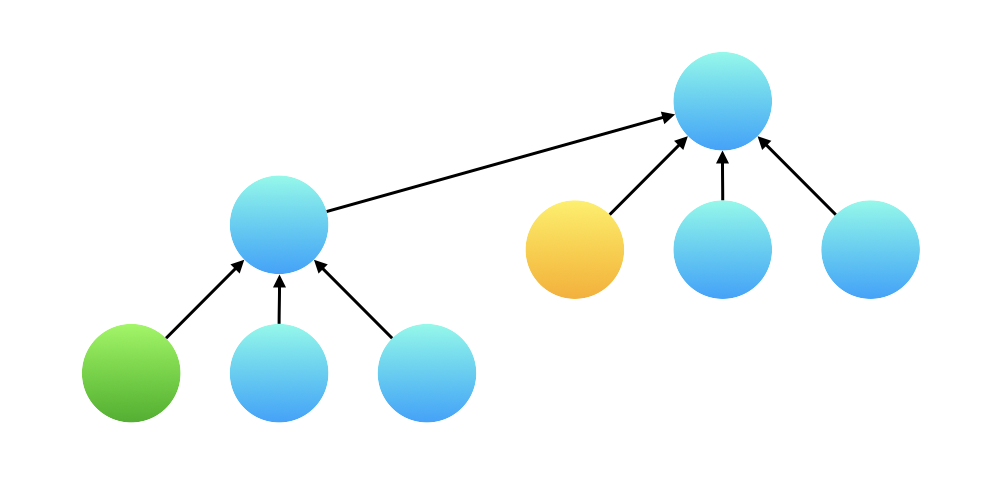
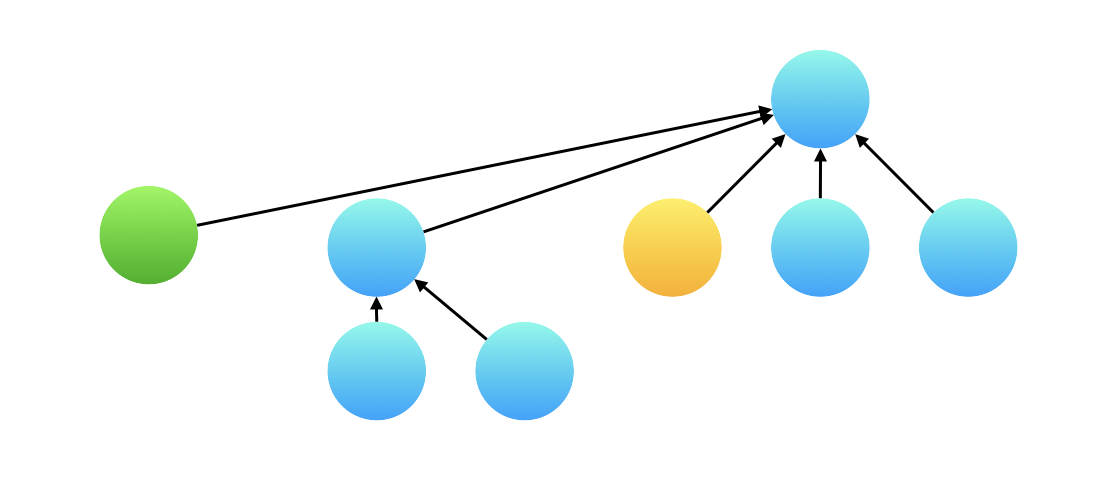
绿色节点和黄色节点并不在同一级上。这时需要进行路径压缩,让绿色节点直接指向最终的根节点
public double[] calcEquation(List<List<String>> equations, double[] values, List<List<String>> queries) {
int equationLen = equations.size();
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(equationLen * 2); // 最大可能有2*equationLen个节点
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < equationLen; i++) {
List<String> list = equations.get(i);
String s1 = list.get(0);
String s2 = list.get(1);
// 将string转化为整数
if (!map.keySet().contains(s1)) {
map.put(s1, index++);
}
if (!map.keySet().contains(s2)) {
map.put(s2, index++);
}
unionFind.union(map.get(s1), map.get(s2), values[i]);
}
int querieLen = queries.size();
double[] ret = new double[querieLen];
for (int i = 0; i < querieLen; i++) {
int i1 = map.getOrDefault(queries.get(i).get(0), -1);
int i2 = map.getOrDefault(queries.get(i).get(1), -1);
if (i1 == -1 || i2 == -1) ret[i] = -1.0d;
else ret[i] = unionFind.isConnected(i1, i2);
}
return ret;
}
// 并查集
private class UnionFind {
int[] parent;
double[] weight;
public UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
weight = new double[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i; // 在最开始每个节点的根节点是自己
weight[i] = 1.0d;
}
}
public void union(int x, int y, double value) {
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if (rootX == rootY) return;
// 修改rootX的父节点以及weight
parent[rootX] = rootY;
weight[rootX] = weight[y] * value / weight[x];
}
// 寻找根节点,路径压缩
public int find(int n) {
// 当前节点不是根节点
if (n != parent[n]) {
int father = parent[n];
// 寻找直接上级的根节点
parent[n] = find(father);
// 更新权值
weight[n] *= weight[father];
}
return parent[n];
}
public double isConnected(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if (rootX == rootY) {
return weight[x] / weight[y];
} else {
return -1.0d;
}
}
}
11.2 省份数量
There are n cities. Some of them are connected, while some are not. If city a is connected directly with city b, and city b is connected directly with city c, then city a is connected indirectly with city c.
A province is a group of directly or indirectly connected cities and no other cities outside of the group.
You are given an n x n matrix isConnected where isConnected[i][j] = 1 if the ith city and the jth city are directly connected, and isConnected[i][j] = 0 otherwise.
Return the total number of provinces.
Example 1:
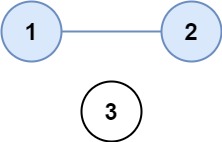
Input: isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 2 Example 2:
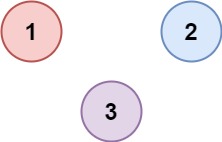
Input: isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 3
采用并查集,最后返回所有parent[n] == n的节点数量即可
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) {
int n = isConnected.length;
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (isConnected[i][j] == 1) {
unionFind.union(i, j);
}
}
}
return unionFind.nums();
}
private class UnionFind {
int[] parent;
private UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
private int find(int n) {
if (parent[n] != n) {
int origin = parent[n];
int root = find(origin);
parent[n] = root;
}
return parent[n];
}
private void union(int x, int y) {
if (find(x) == find(y)) return;
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
parent[rootX] = rootY;
}
private int nums() {
int n = parent.length;
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (find(i) == i) ret++;
}
return ret;
}
}
11.3 最小体力消耗路径
You are a hiker preparing for an upcoming hike. You are given heights, a 2D array of size rows x columns, where heights[row][col] represents the height of cell (row, col). You are situated in the top-left cell, (0, 0), and you hope to travel to the bottom-right cell, (rows-1, columns-1) (i.e., 0-indexed). You can move up, down, left, or right, and you wish to find a route that requires the minimum effort.
A route’s effort is the maximum absolute difference in heights between two consecutive cells of the route.
Return the minimum effort required to travel from the top-left cell to the bottom-right cell.
Example 1:
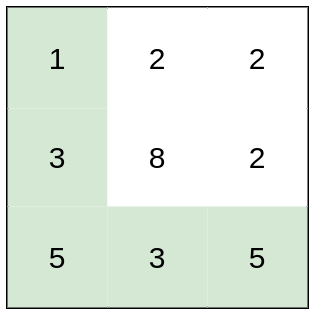
Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] Output: 2 Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells. This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3. Example 2:
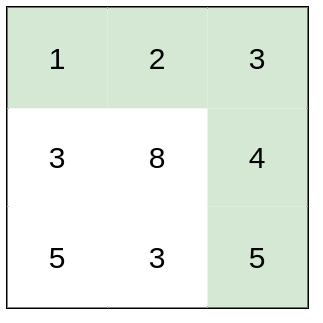
Input: heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: The route of [1,2,3,4,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 1 in consecutive cells, which is better than route [1,3,5,3,5]. Example 3:
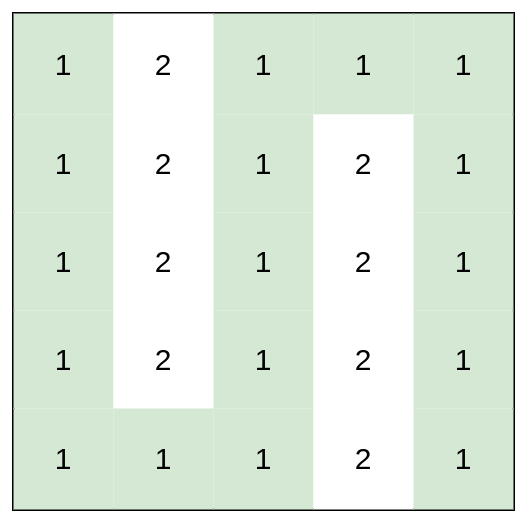
Input: heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] Output: 0 Explanation: This route does not require any effort.
注意:这道题不能使用动态规划,因为路径的连接是可以上下左右四个方向进行的,无法使用动态规划进行递推(在遍历的过程中当前状态取决于之前的状态和之后的状态)。
采用并查集,先找到所有的edge,并且将edge按照权值(两个height的差)从小到大排序,不断从小到大添加edge,判断左上角和右下角何时能够连通,如果能够连通就返回当前添加的edge的权值
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int rows = heights.length;
int cols = heights[0].length;
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(rows * cols);
List<int[]> edges = new ArrayList<>();
for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < cols; col++) {
int index = row * cols + col;
if (row + 1 < rows) {
edges.add(new int[] {index, (row + 1) * cols + col, Math.abs(heights[row][col] - heights[row + 1][col])});
}
if (col + 1 < cols) {
edges.add(new int[] {index, row * cols + col + 1, Math.abs(heights[row][col] - heights[row][col+ 1])});
}
}
}
Collections.sort(edges, (i1, i2) -> (i1[2] - i2[2]));
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
int[] edge = edges.get(i);
unionFind.union(edge[0], edge[1]);
if (unionFind.isConnected(0, rows * cols - 1)) {
return edge[2];
}
}
return 0;
}
private class UnionFind {
int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if (rootX == rootY) return;
parent[rootX] = parent[rootY];
}
public int find(int n) {
if (n != parent[n]) {
int origin = parent[n];
parent[n] = find(origin);
}
return parent[n];
}
public boolean isConnected(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
}
11.4 交换字符串中的元素
You are given a string s, and an array of pairs of indices in the string pairs where pairs[i] = [a, b] indicates 2 indices(0-indexed) of the string.
You can swap the characters at any pair of indices in the given pairs any number of times.
Return the lexicographically smallest string that s can be changed to after using the swaps.
Example 1:
Input: s = “dcab”, pairs = [[0,3],[1,2]] Output: “bacd” Explaination: Swap s[0] and s[3], s = “bcad” Swap s[1] and s[2], s = “bacd” Example 2:
Input: s = “dcab”, pairs = [[0,3],[1,2],[0,2]] Output: “abcd” Explaination: Swap s[0] and s[3], s = “bcad” Swap s[0] and s[2], s = “acbd” Swap s[1] and s[2], s = “abcd” Example 3:
Input: s = “cba”, pairs = [[0,1],[1,2]] Output: “abc” Explaination: Swap s[0] and s[1], s = “bca” Swap s[1] and s[2], s = “bac” Swap s[0] and s[1], s = “abc”
考虑采用并查集,将pairs中所有能够被连接的位置视为一个集合,找到所有这样的集合,然后分别对位置集合所对应的字符进行排序,再映射到原先相应的位置上去即可。
public String smallestStringWithSwaps(String s, List<List<Integer>> pairs) {
int len = s.length();
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(len);
for (int i = 0; i < pairs.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> list = pairs.get(i);
int i1 = list.get(0);
int i2 = list.get(1);
if (unionFind.find(i1) < unionFind.find(i2)) {
unionFind.union(i2, i1);
} else {
unionFind.union(i1, i2);
}
}
List<List<Integer>> set = unionFind.sets();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
for (int i = 0; i < set.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> list = set.get(i);
List<Character> charList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int index : list) {
charList.add(s.charAt(index));
}
Collections.sort(charList, (c1, c2) -> ((int) c1 - (int) c2));
for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {
int index = list.get(j);
sb.setCharAt(index, charList.get(j));
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
private class UnionFind {
int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if (rootX == rootY) return;
parent[rootX] = parent[rootY];
}
public int find(int n) {
if (n != parent[n]) {
int origin = parent[n];
parent[n] = find(origin);
}
return parent[n];
}
public List<List<Integer>> sets() {
int n = parent.length;
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int index = 0;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (find(i) == i) {
List<Integer> ls = new ArrayList<>();
ls.add(i);
ret.add(ls);
map.put(i, index++);
} else {
List<Integer> list = ret.get(map.get(find(i)));
list.add(i);
}
}
return ret;
}
}
12 排序重写Comparator模板
给定一个整数 n, 返回从 1 到 n 的字典顺序。
例如,
给定 n =1 3,返回 [1,10,11,12,13,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] 。
请尽可能的优化算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度。 输入的数据 n 小于等于 5,000,000。
public List<Integer> lexicalOrder(int n) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>(){ {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
add(i + 1);
}
}};
Collections.sort(ret, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return String.valueOf(o1).compareTo(String.valueOf(o2));
}
});
return ret;
}